1. Definition:
The bulk density or dry density of soils is not a constant value, it could be changed in relation with the moisture content of soils and the compaction effort.
|
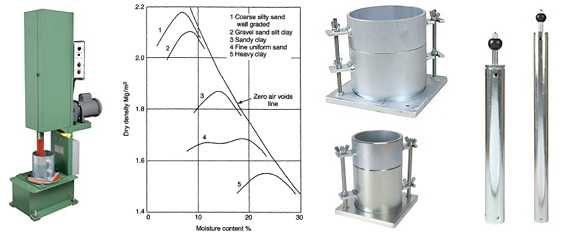
In order to realize the relationship between the moisture content and the compactness of soils, the compaction test is used (so called Proctor test) and its result is the compaction curve — a relationship between the dry density and its relevant moisture content (see a picture on the left). Two important parameters should be derived from this curve: maximum dry density (denoted by MDD) and its corresponding optimum moisture content (denoted by Wopt). |
|
| Compaction curve (after BS 1377 : 1990 - Part 4) |
The gradation also affects to the compactness of a given soil sample. This relationship is demonstrated on the picture below:
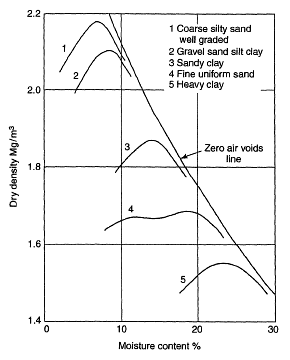
|
Some important points should be taken into account:
a) The compaction curve is a monotonic curve with one peak and two asymmetrical sides (one side with a steep slope and the other is more gentle). b) The right side of the compaction curve theoretically never crosses the zero air voids line (ZAV line). c) The more the clay fraction the lower maximum dry density and the higher optimum moisture content. d) The more uniform gradation the lower maximum dry density and vice versa. e) To a fine sand of poorly graded, the compaction curve represents a bimodal structure (see the curve No. 4 on picture on the left). However the true maximum dry density should be the value at the higher moisture content (approx. 20%, not a value of 12% on the adjacent picture). |
|
| Relationship between moisture content and dry density |
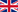
2. Apparatus:

|

|

|

|

|
| Automatic compactor |
Rammer for standard Proctor test | Rammer for modified Proctor test | Mould for standard Proctor test |
Mould for modified Proctor test |
| (Source: www.humboldt.com) | ||||
3. Brief comparison of apparatus, methods for different standards
| Applied Standard |
Method of compaction |
Dimension of mould (D × H) mm |
Rammer mass (kg) |
Falling distance (cm) |
Number of layers |
Blows per layer |
| TCVN | Standard | 100.0 × 127.0 | 2.5 | 30 | 3 | different blows for different soil types |
| Modified | 125.0 × 127.0 | 4.5 | 45 | 5 | 55 | |
| ASTM | Standard rammer (Method A and B) |
101.6 × 116.4 | 2.5 | 30 | 3 | 25 |
| Standard rammer (Method C) |
152.4 × 116.4 | 2.5 | 30 | 3 | 56 | |
| Modified rammer (Method A and B) |
101.6 × 116.4 | 4.5 | 45 | 5 | 25 | |
| Modified rammer (Method C) |
152.4 × 116.4 | 4.5 | 45 | 5 | 56 | |
| BS | Standard mould, standard rammer |
105.0 × 115.5 | 2.5 | 30 | 3 | 27 |
| Standard mould, modified rammer |
105.0 × 115.5 | 4.5 | 45 | 5 | 27 | |
| CBRmould, standard rammer |
152.0 × 127.0 | 2.5 | 30 | 3 | 62 | |
| CBRmould, modified rammer |
152.0 × 127.0 | 4.5 | 45 | 5 | 62 |
4. Referred standards:
a) ASTM D698 : Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort
b) ASTM D1557 : Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Modified Effort